Electrophoresis
(Science: technique) separation of ionic molecules, (principally proteins) by the differential migration through a gel according to the size and ionic charge of the molecules in an electrical field. High resolution techniques normally use a gel support for the fluid phase.
Examples of gels used are starch, acrylamide, agarose or mixtures of acrylamide and agarose. Frictional resistance produced by the support causes size, rather than charge alone, to become the major determinant of separation.
Smaller molecules with a more negative charge will travel faster and further through the gel toward the anode of an electrophoretic cell when high voltage is applied. Similar molecules will group on the gel. They may be visualised by staining and quantitated, in relative terms, using densitometers which continuously monitor the photometric density of the resulting stain.
The electrolyte may be continuous (a single buffer) or discontinuous, where a sample is stacked by means of a buffer discontinuity, before it enters the running gel/ running buffer. The gel may be a single concentration or gradient in which pore size decreases with migration distance.
in sds gel electrophoresis of proteins or electrophoresis of polynucleotides, mobility depends primarily on size and is used to determined molecular weight. In pulse field electrophoresis, two fields are applied alternately at right angles to each other to minimise diffusion mediated spread of large linear polymers.
See: electrofocussing, pulse field electrophoresis
Dictionary > Electrophoresis
You will also like...

Genetics – Lesson Outline & Worksheets
Topics Modules Quizzes/Worksheets Description Introduction to Genetics Genetics – Definition: Heredity and ..

Regulation of Biological Systems
Regulation of Biological Systems tutorials are focused on the modulation of biological systems from cell to population l..

Ecology & Biodiversity: New Zealand Flora & Fauna
New Zealand is known for its unique biodiversity, caused by its remarkable geography and geologic history. Breaking away..
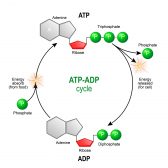
ATP & ADP – Biological Energy
ATP is the energy source that is typically used by an organism in its daily activities. The name is based on its structu..
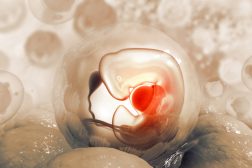
Growth and Development of a Human Baby
Upon fertilization, a zygote forms and develops into an embryo. This tutorial elaborates on the growth and development f..

Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genes are expressed through the process of protein synthesis. This elaborate tutorial provides an in-depth review of the..
