Definition
noun, plural: effectors
(biochemistry) A molecule that binds to a protein and affects the function of that protein
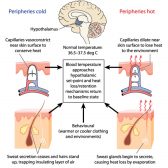
(physiology) An organ, a gland, or a muscle that can respond and becomes active in response to a stimulus (e.g. nerve impulse)
(physiology) The part of a nerve carrying a stimulus to a muscle, gland, organ, etc., and affects the function of the latter
Supplement
In biochemistry, an effector is that molecule that binds to a specific protein, and regulates the latter’s biological activity. An effector molecule acts as a ligand that is capable of increasing or decreasing the activity of that protein. It can also regulate the activity of certain mRNA molecules (e.g. riboswitches), gene expression, and cell signaling. The main types of effectors are the activators and the inhibitors. Examples of effectors are as follows: (1) allosteric effectors, (2) bacterial effectors, and (3) fungal effectors (e.g. apoplastic effectors and cytoplasmic effectors).
In other biological contexts, the term effector is used to describe an organ, a gland, or a muscle that responds to a nerve impulse.
Word origin: Latin, equivalent to effec-, efficere, effectus (the carrying out) + –tor ()
Variant(s):
- effecter
See also:
- activator
- inhibitor
- gene expression
- cell signaling
- cell-mediated immunity
- adrenoceptor
- efferent fibres
- corepressor
- pathway
- killer cells
Related term(s):
- effect