Search Results for: transmembrane_proteins
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
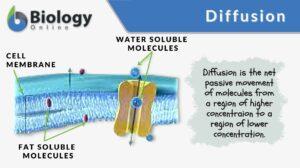
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Membrane protein
Definition noun, plural: membrane proteins A type of protein that is attached to, or associated with, a biological... Read More
Microfilament
Definition noun plural: microfilaments mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī'krō-fil'ă-mĕnts A thin, helical, single-stranded... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
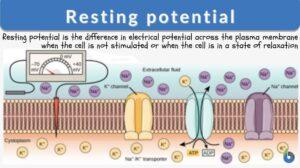
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Transmembrane proteins
transmembrane protein (Science: cell biology) A protein subunit in which the polypeptide chain is exposed on both sides of... Read More
Transmembrane protein
Definition noun, plural: transmembrane proteins A protein that spans the entire biological... Read More
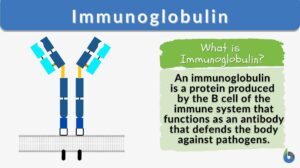
Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin Definition An immunoglobulin is a globulin molecule produced by the immune cells, for the body's defense... Read More
Integral membrane protein
Definition noun A protein molecule (or assembly of proteins) that is permanently attached or firmly anchored in the plasma... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Polarization
Definition noun (general) The condition of polarity (biology) The process or act of producing positive and negative... Read More
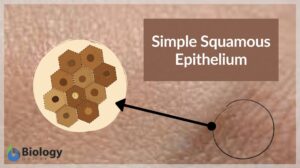
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
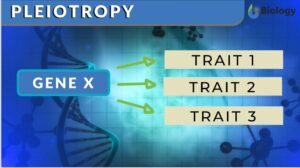
Pleiotropy
Pleiotropy Definition When one single gene starts affecting multiple traits of living organisms, this phenomenon is known... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
Beta barrel
Definition noun, plural: beta barrels A large β-sheet that twists and coils to form a closed structure where the first... Read More
Alpha-helix
Definition noun, plural: alpha helices A right-handed coiled conformation common in many proteins in which the resulting... Read More
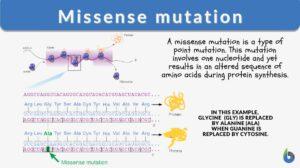
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Integral protein
Definition noun, plural: integral proteins A protein molecule or protein assembly permanently attached in biological... Read More
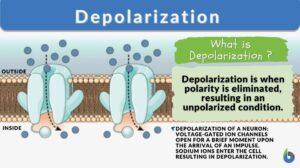
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
Blood-brain barrier
Definition noun A semipermeable membrane that serves as a selective barrier separating the circulating blood and the... Read More
Gated ion channel
(Science: physiology) transmembrane proteins of excitable cells, that allow a flux of ions to pass only under defined... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Transportase
transportase --> transport protein (Science: protein) A class of transmembrane protein that allows substances to cross... Read More