Search Results for: strong
Covalent bond
Covalent Bond Definition What is a covalent bond? In chemistry and other fundamental science fields, a covalent bond is... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Mutualistic symbiosis
Mutualistic Symbiosis Definition In order to understand what a mutualistic symbiotic relationship means, we will break down... Read More
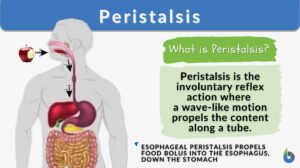
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
Transition
Definition noun, plural: transitions (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by the replacement of a purine by... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
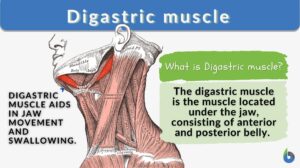
Digastric muscle
Digastric Definition The digastric muscle is a paired muscle located under the jaw, consisting of the anterior and... Read More
A Balanced Diet – Minerals and Proteins
Minerals Various minerals in the Earth's crust are required for a healthy balanced diet. These inorganic compounds have... Read More
New Zealand’s Unique Flora
By: Maria Victoria Gonzaga In the previous lesson, we've come to know some of the most fascinating endemic... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Ionic bond
Definition noun plural: ionic bonds A type of chemical bond in which atoms, ions, or molecules are held together by... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
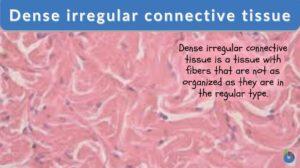
Dense irregular connective tissue
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Definition Dense irregular connective tissue is one of the two major types of dense... Read More
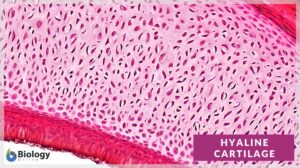
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Apical Dominance
a condition where vertical growth supercedes lateral growth in a plant. this is controlled by auxins, where in high... Read More
Phenol coefficient
Chemical disinfectants are categorized based on the power of their disinfection for microbes and viruses. Strong... Read More
Pollen Grain
What are Pollen Grains? Plants are unique structures and so they carry out mechanisms in special ways. Fertilization in... Read More
Three-chambered heart
Three-chambered heart congenital abnormality in which there may be a single atrium with two ventricles or a single ventricle... Read More
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
Renaturation
Definition noun, plural: renaturations (molecular biology) The conversion of denatured protein or nucleic acid to its native... Read More
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is... Read More
Joints of pelvic girdle
The joints of pelvic girdle, in anatomy, are the joints that unite the sacrum and the two hip bones, forming the pelvic... Read More
Refractory Period
(neurology) the time after a neuron fires or a muscle fiber contracts during which a stimulus will not evoke a response.The... Read More