Search Results for: quantity
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
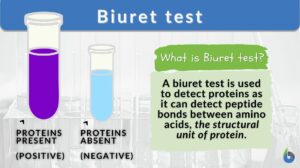
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Renewable resource
Definition noun A type of natural resource that can be replenished or takes a rather short period of time for nature to... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Multiplication
multiplication 1. The act or process of multiplying, or of increasing in number; the state of being multiplied; as, the... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
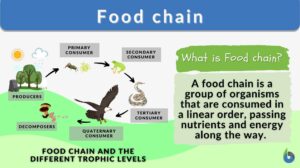
Food chain
Everything is a cycle in life. The way organisms consume their food also follows a cycle. This is usually described as the... Read More
Community Patterns
By: Maria Victoria Gonzaga In the previous lesson, we learned what a population is, its attributes, and processes... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
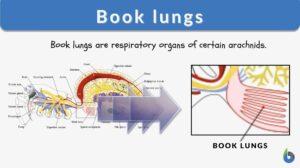
Book lungs
Book Lungs Definition Lungs are known as the organs that help organisms breathe. When we think of lungs, we think of the... Read More
Independent variable
Independent Variable Definition To define an independent variable, let us first understand what a variable is. The word... Read More
Ecosystem diversity
Ecosystem Diversity Definition What is ecosystem diversity? Ecosystem diversity deals with the study of different... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
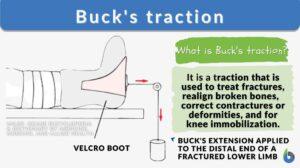
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
Freshwater Ecology
Freshwater ecology focuses on the relations of aquatic organisms to their freshwater habitats. There are two forms of... Read More
Radial immunodiffusion
Definition noun A quantitative immunodiffusion technique used to detect the level of protein (antigen) in a sample by... Read More