Search Results for: physiologic
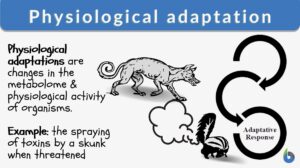
Physiological adaptation
If we look over evolutionary history, we find that it’s neither the most genius and intelligent nor the strongest and the... Read More
Physiological
Definition "adjective'' (1) Of, or pertaining to physiology or normal functioning of an organism. (2) (pharmacology)... Read More
Hypotonicity
Definition noun The state of being hypotonic, i.e. having lesser degree of tone or tension Supplement In biology, tonicity... Read More
Deglutology
Definition noun The scientific or medical study of the processes and pathophysiology of deglutition Supplement Deglutology... Read More
Pseudovitamin b12
pseudovitamin B12 (Science: biochemistry) Cobamide cyanide phosphate, 3'-ester with 7-alpha-d-ribofuranosyladenine, inner... Read More
Wasted ventilation
wasted ventilation That part of the pulmonary ventilation which is ineffective in exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide with... Read More
Hypertonicity
Definition noun The state of being hypertonic, i.e. having a greater degree of tone or tension Supplement In biology,... Read More
Mobilization
mobilization 1. Making movable; restoring the power of motion in a joint. 2. The act or the result of the act of mobilizing;... Read More
Gap 0 phase
Definition noun The phase in the cell cycle wherein the cell is in inactive or non-cycling state following cell... Read More
Sphenopalatine ganglioneuralgia
Definition noun The medical or scientific term for brain freeze Supplement The sphenopalatine ganglioneuralgia is a type of... Read More
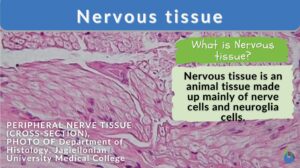
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Uterine cycle
Definition noun The cycle that depicts the changes in the endometrial lining occurring during a menstrual cycle, and is... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Polycythemia
Definition noun An increase in the number of circulating erythrocytes in the blood above the minimum normal... Read More
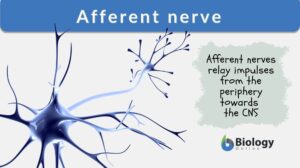
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
Inflammatory response
Definition noun, plural: inflammatory responses (medicine) A response of the body to an injurious agent, characterized by... Read More
Menstruation
Definition noun The periodic physiologic discharge through the vagina of blood, cervical mucus, vaginal secretions, and... Read More
Resorption
resorption (Science: physiology) The loss of substance through physiologic or pathologic means, such as loss of dentin and... Read More
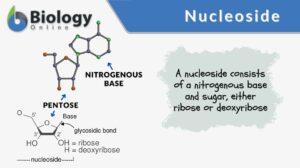
Nucleoside
Nucleoside Definition A nucleoside is a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) bound to a pentose sugar ribose or... Read More
End-point nystagmus
End-point nystagmus a jerky, physiologic nystagmus occurring in a normal individual when attempts are made to fixate a point... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Voluntary dehydration
voluntary dehydration That physiologic lag or deficit that results when sensations of thirst are not strong enough to bring... Read More
Tissue perfusion
Definition noun The volume of blood that flows through a unit quantity of the tissue, and is often expressed in unit: ml... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More