Search Results for: muscle_cells
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
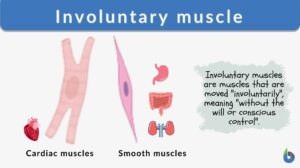
Involuntary muscle
A muscle act typically either under the control of the will or without conscious control. Muscles that can be controlled at... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
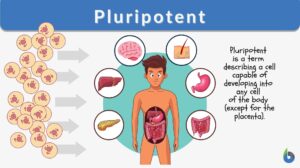
Pluripotent
Pluripotent Definition What is pluripotent? In biology, the term "pluripotent" means capable of developing into... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Cardiac muscle
Definition noun, plural: cardiac muscles (1) The heart muscle of the vertebrates (2) myocardium Supplement The muscles of... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Muscle cell
Definition noun, plural: muscle cells Any of the long, tubular mature contractile cells that make up the muscle... Read More
Muscle tissue
Definition noun, plural: muscle tissues An animal tissue capable of contracting, and therefore enables movement or tension... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
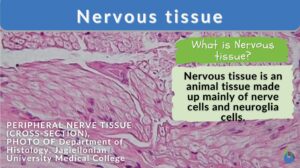
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
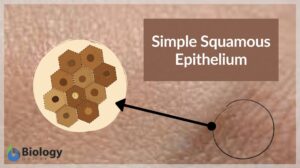
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More