Search Results for: liver_circulation
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Angiotensinogen
Definition noun An alpha-2 globulin protein that is found in the bloodstream and release into circulation mainly by the... Read More
Endocrine gland
Definition noun, plural: endocrine glands Any of the ductless glands secreting hormones that are released directly into... Read More
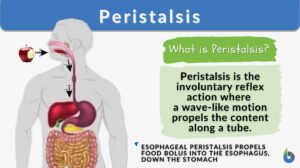
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
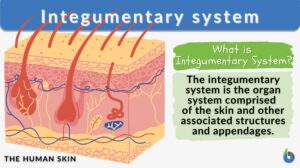
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Spongy bone
Spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone or trabecular bone, is a type of bone tissue found at the ends of long bones and... Read More
Plasma volume
Definition noun The total volume of the blood plasma in the circulatory system Supplement The blood is comprised of plasma... Read More
Vasopressin
Definition noun, plural: vasopressins An antidiuretic peptide hormone produced by the magnocellular and the parvocellular... Read More
Erythroblastosis fetalis
Definition noun A medical condition in the fetus or newborn in which many erythroblasts are released in fetal blood from the... Read More
Argipressin
Definition noun, plural: argipressins A vasopressin that has an amino acid sequence:... Read More