Search Results for: intestinal_15_kd_protein
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Digestive Enzymes
Have you ever thought about what happens to the food after you have taken it into your mouth? How those big steak pieces... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
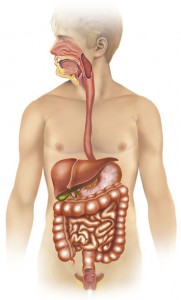
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
“Mutualism factor” could explain why body does not attack normal flora
When sadness reeks in and you feel as if you are all by yourself, think again. That is because you are never alone. As a... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Microvillus
Definition noun, plural: microvilli Any of the minute hairlike structures projecting from the exposed surface of the cell in... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
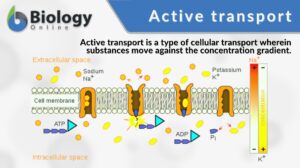
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Cystic fibrosis
Definition noun An autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the gene that encodes for cystic fibrosis... Read More
Phenylalanine
phenylalanine (Science: amino acid) One of the amino acids which the body cannot manufacture itself, but must acquire from... Read More
How Celiac Disease Affects The Digestive System
Celiac disease is a condition that affects the digestive systems of many individuals all over the world, and in this... Read More