Search Results for: independent
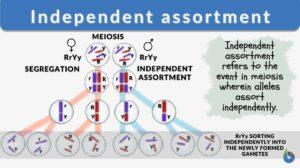
Independent Assortment
Independent Assortment Definition Independent assortment refers to the alleles or genes that sort into the newly formed... Read More
Independent variable
Independent Variable Definition To define an independent variable, let us first understand what a variable is. The word... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
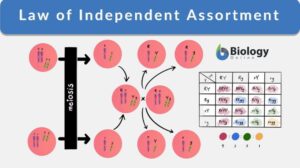
Law of Independent Assortment
Law of Independent Assortment Definition noun (genetics) Mendelian law stating that for every pair of unit factors, each... Read More
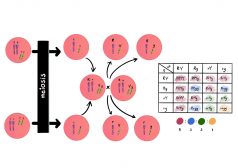
Independent Assortment and Crossing Over
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. The previous tutorial investigates the process of meiosis, where... Read More
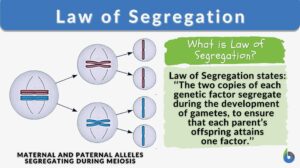
Law of Segregation
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance The father of genetics, Gregor Mendel, reported his findings in 1860 that initially were... Read More
Density Independent Factor
Definition noun, plural: density independent factors (ecology) A factor that affects the size of a population independent or... Read More
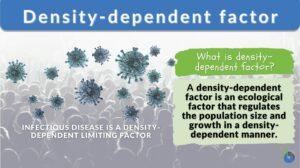
Density dependent factor
Density-dependent factors are the limiting factors of an ecosystem that regulate population growth in a density-dependent... Read More
Density dependent limiting factor
What Is A Density-Dependent Limiting Factor? Density-dependent limiting factors are limiting factors, which, depending on... Read More
Anchorage-independent cell
Definition noun A cell that has lost the need for anchorage dependence, which is essential for cell growth, division, and... Read More
Dependent variable
Definition noun, plural: dependent variables (mathematical modeling) The variable in a functional relation whose value is... Read More
Genetics – Lesson Outline & Worksheets
Topics Modules Quizzes/Worksheets Description Introduction to Genetics Genetics - Definition:... Read More
Population Regulation in an Ecosystem
Darwin focused some of this work in regards to the population size of a species, and what factors may affect them. He... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
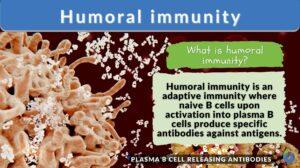
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
Limiting factor
Limiting Factor Definition A limiting factor refers to any of the factors (variables) in an environment capable of limiting... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
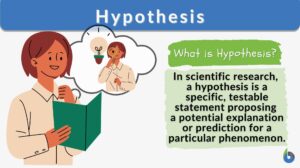
Hypothesis
What Is Hypothesis? A scientific hypothesis is a foundational element of the scientific method. It's a testable statement... Read More
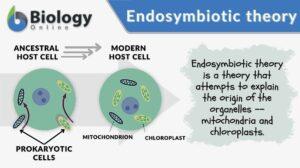
Endosymbiotic theory
A eukaryotic cell is distinct from a prokaryotic cell by the presence of membrane-bound cellular structures called... Read More
Population Growth and Survivorship
By: Maria Victoria Gonzaga Previously, we learned about biodiversity and endemism. Now, let's look at the... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Polygenic trait
Polygenic Trait Definition Polygenic trait refers to a trait that is controlled by multiple non-allelic genes. These genes... Read More
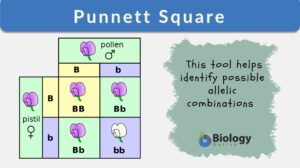
Punnett Square
Punnett Square Definition A tool that helps to show all possible allelic combinations of gametes in a cross of parents with... Read More
Mendel’s laws: definitions
Genetics - a branch of biology that deals with the study of heredity and variations Variations - differences amongst the... Read More
Controlled variable
Definition noun, plural: control variables A variable that remains unchanged or held constant to prevent its effects on the... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Fragmentation
Fragmentation Definition What is fragmentation? In general, fragmentation refers to the state or the process of breaking... Read More
Allopatric speciation
We can define speciation as a process by which the novel genetically independent group of organisms are formed through the... Read More
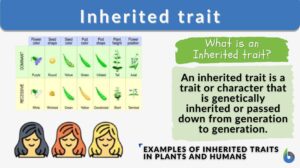
Inherited traits
What are Inherited Traits? The characteristics or traits that are passed from parents to offspring are known as inherited... Read More
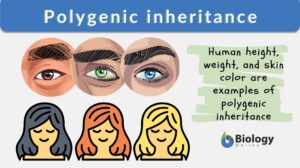
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
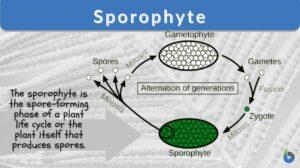
Sporophyte
Sporophyte Definition What is a sporophyte? Accordingly, the sporophyte is the plant generation that produces spores. To... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Control variable
Definition noun, plural: control variables A variable that remains unchanged or held constant to prevent its effects on... Read More