Search Results for: food_storage
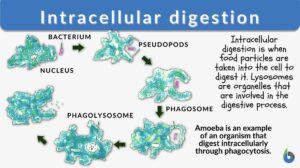
Intracellular digestion
Intracellular Digestion Definition What is intracellular digestion? ‘Intra’ means "inside" and ‘cellular’ pertains... Read More
Contamination
Contamination Definition Contamination, sometimes interchanged with pollution, is the existence of live things or... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
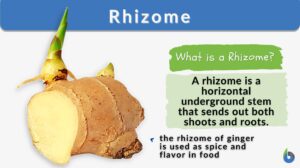
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Human Biology – Food and Digestion
Food is what is required by humans to grow and survive, and provide a 'fuel' for the energy needed in our biological... Read More
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
Digestive Enzymes
Have you ever thought about what happens to the food after you have taken it into your mouth? How those big steak pieces... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Lysosomal enzyme
Definition noun plural: lysosomal enzymes ly·so·somal en·zyme, ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm əl ˈɛnzaɪm (biochemistry) Any of... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Elaioplast
Definition noun, plural: elaioplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores oil Supplement Plastids are organelles involved in... Read More
Amyloplast
Definition noun, plural: amyloplasts (botany) A type of leucoplast found in the cytoplasm of a plant cell, and serves as... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Humans are Omnivores – Evidence
A number of popular myths about vegetarianism sprung with no scientific basis. One example of such a myth is that man is... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Leucoplast
Definition noun, plural: leucoplasts A plastid lacking photosynthetic pigments and involved in various biosynthetic... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More