Search Results for: follows
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
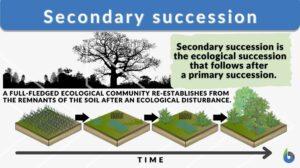
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
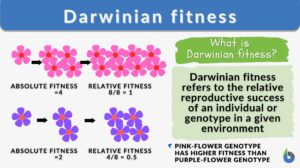
Darwinian fitness
Darwinian Fitness Definition Darwinian fitness refers to the measure of an individual organism's or genotype's reproductive... Read More
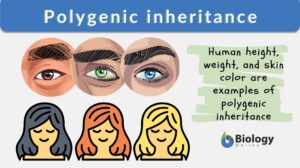
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
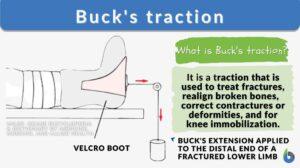
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
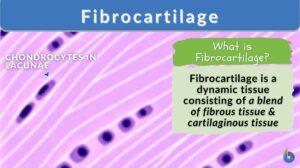
Fibrocartilage
What Is Fibrocartilage? Fibrocartilage is the strongest transitional connective tissue made up of collagen fibers and... Read More
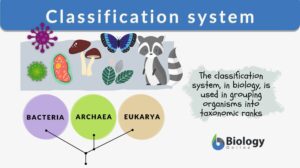
Classification system
Classification Systems Definition In life, many things are classified, that is, to put into categories or groups based on... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
Skeletal system
What is the Skeletal System? How to define a skeleton? The skeletal system is the main framework that gives your body its... Read More
Diazotroph
Definition noun, plural: diazotrophs A microorganism capable of assimilating and fixing atmospheric nitrogen... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
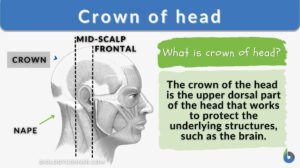
Crown of head
Crown of Head Definition The crown of the head is the upper dorsal part (or area) of the head. Several creatures have... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
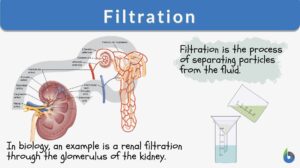
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Lymph nodes
Lymph nodes definition Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs located in different parts of the body and act as... Read More
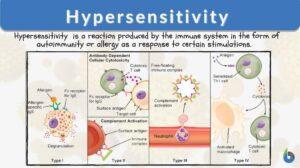
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity Definition Hypersensitivity is the exaggerated immune response to protect the human from foreign bodies... Read More
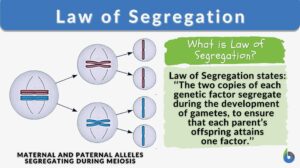
Law of Segregation
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance The father of genetics, Gregor Mendel, reported his findings in 1860 that initially were... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More




















![Biology n., [baɪˈɑlədʒi] Definition: scientific study of life](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/biology-definition-and-branches-of-biology-300x168.jpg)