Search Results for: erythrocytes
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Oxyhemoglobin
Definition noun, plural: oxyhemoglobins A bright red hemoglobin carrying oxygen molecule Supplement One of the main... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Hemoglobin
Definition noun, plural: hemoglobins A biomolecule made up of haeme (i.e. oxygen-carrying, nonprotein, ferrous component)... Read More
Sphingolipidosis
Definition noun, plural: sphingolipidoses A lysosomal disease due to an abnormal sphingolipid... Read More
Sphingolipid
Definition noun plural: sphingolipids sphin·go·lip·id A type of lipid with a sphingoid base (e.g. sphingosine and... Read More
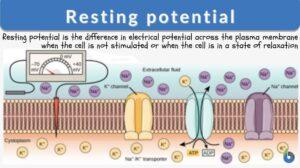
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Streptolysin S
Definition noun A nonantigenic, oxygen-stable β-hemolytic enzyme produced by some bacteria, especially... Read More
Incomplete antibody
Incomplete antibody --> univalent antibody An incomplete form of antibody that may coat antigen, but which according to... Read More
Phytohemagglutinin
Definition noun, plural: phytohemagglutinins A hemagglutinin derived from a plant, especially... Read More
Fraser-lendrum stain
Fraser-lendrum stain (Science: technique) For fibrin, a multistaining procedure after Zenker's fixative in which fibrin,... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Rosette formation
rosette formation The in vitro formation of clusters consisting of a cell (usually a lymphocyte) surrounded by antigenic... Read More
Accole forms
Accole forms --> applique forms a term applied to the manner in which the ring stage of plasmodium falciparum parasitises... Read More
Ferrous lactate
Definition noun A greenish white crystal or (powder) made up of iron (Fe2+) and lactate anions Supplement Ferrous lactate is... Read More
Plaque assay
Definition noun An assay used for virus isolation and purification, and to determine viral titers. Supplement The plaque... Read More
Erythrocythemia
Definition noun (1) An increase in the number of circulating erythrocytes in the blood above the minimum normal level. (2)... Read More
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More