Search Results for: complementary_base_pairing
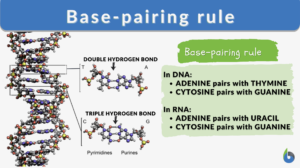
Base-pairing rule
Base-pairing Rules Definition The base-pairing rules are rules that apply during the pairing between one purine and one... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Transcription (biology)
In biology, transcription is the process of transcribing or making a copy of the genetic information stored in a DNA strand... Read More
Thymidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
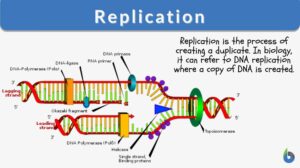
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Complementary base pairing
'''complementary base pairing The standard arrangement of bases in nucleotides in relation to their opposite pairing, such... Read More
Polynucleotide
Definition noun plural: polynucleotides pol·y·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌpɒlɪˈno͞o′klē-ə-tīd A biopolymer comprised of... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Deoxyadenosine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyadenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, deoxyribose and... Read More
Base pairing
Base pairing (Science: molecular biology) The specific hydrogen bonding between purines and pyrimidines in double stranded... Read More
Thymidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and three... Read More
Deoxycytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxycytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Deoxyguanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyguanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
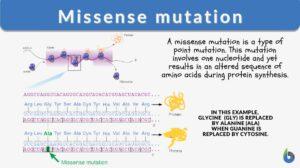
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Deoxyadenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyadenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
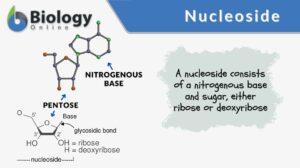
Nucleoside
Nucleoside Definition A nucleoside is a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) bound to a pentose sugar ribose or... Read More
Deoxycytidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxycytidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, deoxyribose and... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Deoxyguanosine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyguanosine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, deoxyribose and... Read More
Oligonucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides ol·i·go·nu·cle·o·tide, ŏl′ĭ-gō-no͞o′klē-ə-tīd A short polymer... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More
Complementary strands
Complementary strands (Science: molecular biology) two single strands of dna in which the nucleotide Sequence is such that... Read More
Guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Cytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Deoxyguanosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyguanosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Dinucleotide
Definition noun plural: dinucleotides di·nu·cle·o·tide, daɪ njuːklɪəˌtaɪd An organic compound comprised of two... Read More
Deoxyadenosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyadenosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, deoxyribose and two... Read More