Search Results for: chemical_bond
Covalent bond
Covalent Bond Definition What is a covalent bond? In chemistry and other fundamental science fields, a covalent bond is... Read More
Hydrogen bond
Definition noun plural: hydrogen bonds A type of chemical bond that is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of... Read More
Ionic bond
Definition noun plural: ionic bonds A type of chemical bond in which atoms, ions, or molecules are held together by... Read More
Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester Bond Definition Phosphodiester bonds are the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid present in the life... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Chemical bond
Definition noun, plural: chemical bonds The attractive force that binds atoms, ions, or molecules in a chemical... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Isopeptide bond
Definition noun, plural: isopeptide bonds A peptide bond formed between a carboxyl group of one amino acid and an amino... Read More
Isomaltose
Definition noun plural: isomaltoses i·so·mal·tose, aɪsoʊˈmɔːltəʊz A disaccharide formed from the combination of... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Inorganic compound
Inorganic Compound Definition An inorganic compound is a chemical compound lacking both carbon-carbon (C-C) and... Read More
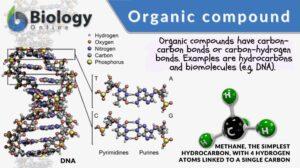
Organic compound
Organic Compound Definition An organic compound is a compound that, in general, contains carbon covalently bound to other... Read More
Cellobiose
Definition noun plural: cellobioses cel·lo·bi·ose, ˌsɛləʊˈbaɪəʊz A disaccharide made up of two glucose... Read More
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
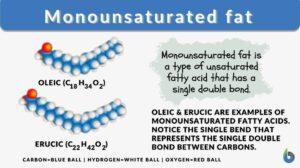
Monounsaturated fat
What is monounsaturated fat? Monounsaturated fats are healthy dietary fats. They are liquid at room temperature. Unlike... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More