Search Results for: blood_pressure
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
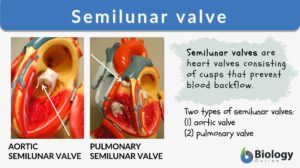
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More
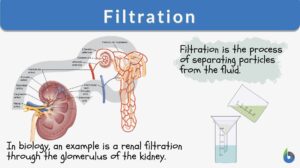
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Blood pressure
Blood pressure (Science: cardiology, physiology) The force that the circulating blood exerts on the walls of the... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
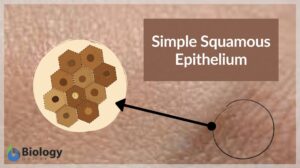
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Fibrinous exudate
What Is Fibrinous Exudate? Fibrinous exudate is a type of exudate (inflammatory fluid) that forms at the site of tissue... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
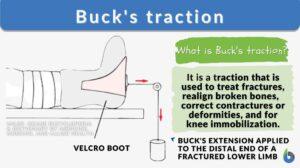
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
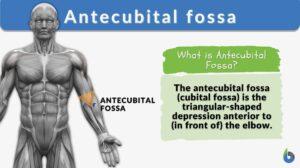
Antecubital fossa
Antecubital Fossa Definition The antecubital fossa or the cubital fossa is the triangular-shaped hollow depression between... Read More
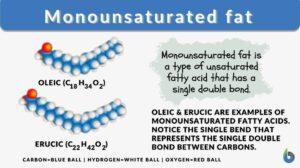
Monounsaturated fat
What is monounsaturated fat? Monounsaturated fats are healthy dietary fats. They are liquid at room temperature. Unlike... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Blood vessel
Definition noun, plural: blood vessels Any of the vessels in cardiovascular system and functions by carrying blood... Read More
Polymorphism
Polymorphism Definition The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs in the population of a species is referred... Read More
Angiotensinogen
Definition noun An alpha-2 globulin protein that is found in the bloodstream and release into circulation mainly by the... Read More
![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)