Search Results for: biochemical_evolution
Sexual selection
What is Sexual Selection? The definition of sexual selection is very interesting in biological terms. The sexual selection... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
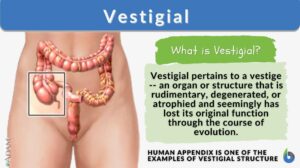
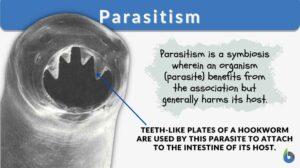
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
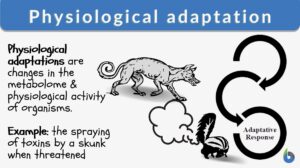
Physiological adaptation
If we look over evolutionary history, we find that it’s neither the most genius and intelligent nor the strongest and the... Read More
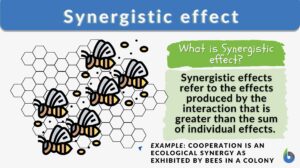
Synergistic effect
Synergistic Effects Definition In biology, synergistic effects are the effects when chemical substances or biological... Read More
Chloroplast
Chloroplast Definition What is chloroplast? In biology, a chloroplast refers to the organelle found within the cell of... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Codominance
Codominance Definition Codominance is a form of inheritance wherein the alleles of a gene pair in a heterozygote are fully... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life ... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Extracellular matrix
Definition noun, plural: extracellular matrices The non-cellular portion of a tissue produced and secreted by cells and... Read More
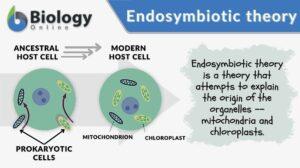
Endosymbiotic theory
A eukaryotic cell is distinct from a prokaryotic cell by the presence of membrane-bound cellular structures called... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More