Search Results for: agar-agar
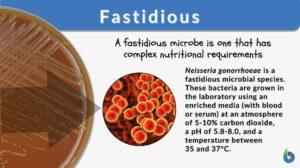
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More
Colony-forming unit
Colony Forming Unit Definition A Colony Forming Unit (CFU) in microbiology and cellular biology refers to a measure of... Read More
Gamma hemolysis
Definition noun Nonhemolytic bacterial colony on blood agar plates. Supplement The hemolytic reactions of streptococci on... Read More
Cultivated yeast
Definition noun, plural: cultivated yeasts Yeast that is grown in cultures for specific purposes such as bread making,... Read More
Differential medium
Differential medium a medium which is used to differentiate different types of microorganisms based on their different... Read More
The consequences of antibiotic use in horticulture
Leading articles Frederick R. Falkiner* Department of Clinical Microbiology, Trinity College, Dublin; Central Pathology... Read More
Streptococcus
Definition noun, plural: streptococci (1) A genus of bacteria characterized by being coccus, Gram-positive, and occurring in... Read More
Streptolysin S
Definition noun A nonantigenic, oxygen-stable β-hemolytic enzyme produced by some bacteria, especially... Read More
Lycinibacillus fusiformis
Definition noun A long rod-shaped obligate aerobe organism that is able to utilize oxygen to metabolize numerous sugars... Read More
Petri dish
Definition noun, plural: Petri dishes A circular dish made of glass or plastic and with a loose-fitting cover, used in... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Melanophore
Definition noun, plural: melanophores A type of pigment cell that, in particular, produce and store... Read More
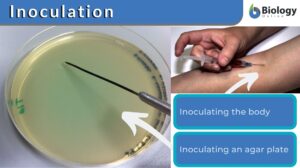
Inoculation
Inoculation Definition In Immunology, inoculation is defined as the process of introducing an antigenic substance or... Read More
Zone of inhibition
Definition noun (microbiology) The clear region around the paper disc saturated with an antimicrobial agent on the agar... Read More
Melanocyte
Definition noun, plural: melanocytes A type of pigment cell that, in particular, produce melanin, and occurs in the... Read More
Axenic culture
Definition noun A microbial culture that contains only one species, variety, or strain of... Read More
Auxanographic method
Auxanographic method a method for the study of bacterial enzymes in which agar is mixed with the material (e.g., starch or... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Substratum
Definition noun, plural: substrata (1) A substrate, i.e. a surface in which the cell attaches to, especially when the cell... Read More
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More
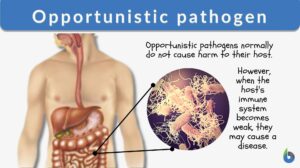
Opportunistic pathogen
Opportunistic Pathogen Definition How do we define opportunistic pathogen? The opportunistic pathogen is an infectious... Read More
Organ culture
Definition noun, plural: tissue cultures (1) The technique of cultivating organ primordia or pieces of tissue in the... Read More
Culture media
Culture media Any liquid or solid preparation made specifically for the growth, storage, or transport of microorganisms or... Read More
Replica plating
replica plating (Science: technique) technique for testing the genetic characteristics of bacterial colonies. A dilute... Read More
Enterobacteriaceae
Definition noun: (taxonomy) A family of gram-negative bacilli that inhabit the large intestine of humans and other... Read More