Search Results for: addition_reaction
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
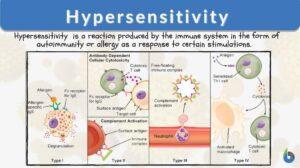
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity Definition Hypersensitivity is the exaggerated immune response to protect the human from foreign bodies... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
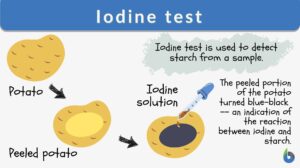
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
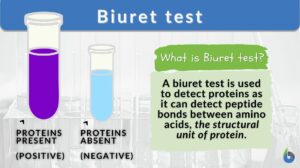
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Hydrolysis
Definition noun (chemistry) (1) A chemical reaction in which the interaction of a compound with water results in the... Read More
Enzymatic hydrolysis
Definition noun A catalytic decomposition of a chemical compound by reaction with water, such as the conversion of... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Limiting factor
Limiting Factor Definition A limiting factor refers to any of the factors (variables) in an environment capable of limiting... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Polymerization
Definition noun, plural: polymerizations The act of process of forming a polymer, especially by chemical reactions that join... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Peptide bond
Definition noun, plural: peptide bonds (1) The covalent bond joining amino acids, particularly at the carboxyl group of... Read More
Proliferative inflammation
proliferative inflammation An inflammatory reaction in which the distinguishing feature is an actual increase in the number... Read More
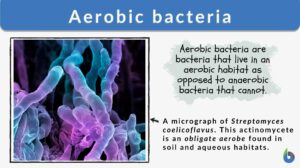
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
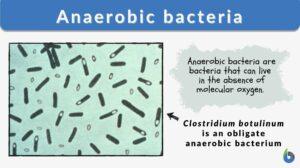
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More